
Radiographic Anatomy of Facial Bones Radiology, Medical radiography, Facial bones
Facial fractures are commonly caused by blunt or penetrating trauma at moderate or high levels of force. Such injuries may be sustained during a fall, physical assault, motor vehicle collision, or gunshot wound. The facial bones are thin and relatively fragile, making them susceptible to injury. Epidemiology

Xray/Face front stock photo. Image of diagnostic, illness 198832
Face X-ray is a method of radiation diagnosis of pathology of facial bones. It is used for visualization of the palatine, sublingual, maxillary, nasal, zygomatic bones and temporomandibular joint.

Xray film of the face frontal, nosechin projection. Sinusitis. — Stock Photo © vanzittoo
A facial X-ray is a series of pictures of the bones in the face. One type of facial X-ray (called a paranasal sinus X-ray series) looks at the air-filled cavities (sinuses) around the nose and eyes. A facial X-ray helps find bone fractures, tumors, foreign objects, infections, and abnormal growths or changes in bone structure or size.
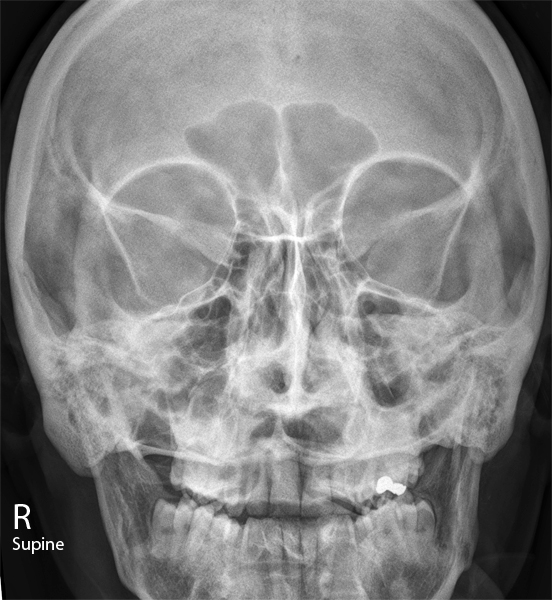
Facial Bone Radiography wikiRadiography
Traditionally, facial x-rays played an important screening role in the evaluation of facial trauma and infection. However, the complex three-dimensional relationship of facial bones and sinus air spaces makes interpretation of plain x-ray difficult.
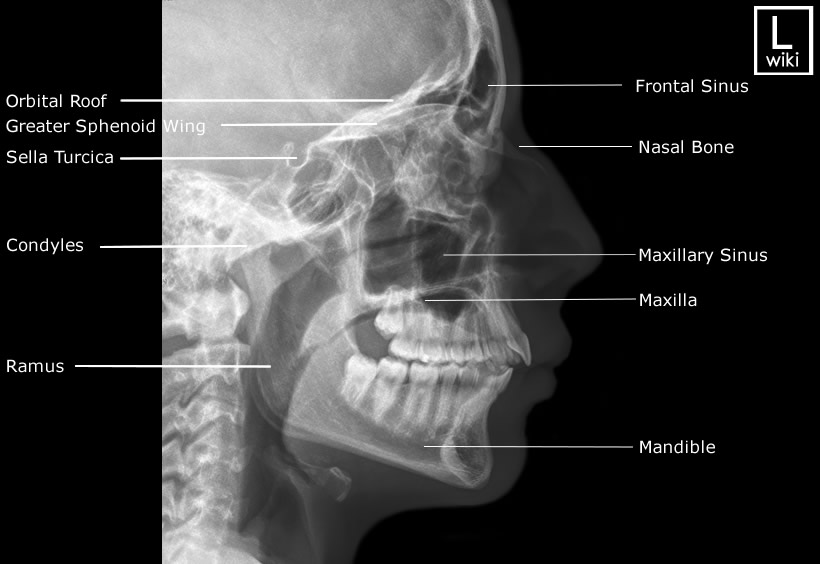
Facial Bones Radiographic Anatomy wikiRadiography
Face - Tripod fracture - OM view. A 'tripod' fracture has 4 visible components - not always all visible. 1 - Orbital floor fracture. 2 - Fracture of the lateral wall of the maxillary antrum. 3 - Zygomatic arch fracture. 4 - Widening of the zygomatico-frontal suture. Increased density of the maxillary antrum is due to it filling with blood.
Xray picturehuman head stock photo. Image of diagnosis 10611516
A skull X-ray is an imaging test doctors use to examine the bones of the skull, including the facial bones, the nose, and the sinuses. See a Body Map of the skull. It's an easy, quick, and.

Face XRay stock photo. Image of face, radiology, patient 1792828
Unofficial implementation of paper 'Face X-ray for More General Face Forgery Detection'. (updating.) This is an unofficial implementation of Lingzhi Li, Jianmin Bao, Ting Zhang, Hao Yang, Dong Chen, Fang Wen, Baining Guo: Face X-Ray for More General Face Forgery Detection. CVPR 2020: 5000-5009.

Front face skull xray image Stock Photo Colourbox
Appearances of facial bone fractures as seen on X-ray. X-ray of facial bones. McGriggor-Campbell fracture lines on facial bone x-rays. Use of OM views - occipitomental X-rays for diagnosis of facial bone fractures. The zygomatic arch looks like an elephants trunk on facial bone X-rays. Description of zygomatic arch fractures, trpod fractures and blow out fractures of the facial bones as seen.

XRay of Skull and Face Stock Image C039/4288 Science Photo Library
A facial X-ray is a series of pictures of the bones in the face. One type of facial X-ray (called a paranasal sinus X-ray series) looks at the air-filled cavities (sinuses) around the nose and eyes. A facial X-ray helps find bone fractures, tumours, foreign objects, infections, and abnormal growths or changes in bone structure or size.

Brace Face
A facial X-ray is a series of pictures of the bones in the face. One type of facial X-ray (called a paranasal sinus X-ray series) looks at the air-filled cavities (sinuses) around the nose and eyes. A facial X-ray helps find bone fractures, tumors, foreign objects, infections, and abnormal growths or changes in bone.

Facial bone xrays
Written on 02/12/2016 , Last updated 31/07/2021 Cite this article as: Tessa Davis . Facial bone x-rays, Don't Forget the Bubbles, 2016. Available at: https://doi.org/10.31440/DFTB.10471 There are two views - occipito-mental view and occipito-mental 30 o view

Facial Bone XRay Anatomy AP by Dr. Naveen Sharma GrepMed
The high cost of portable X-ray machines is also an issue. While they are cheaper than the larger fixed machines, they are still very expensive. The Stop TB Partnership says that the price of.
3d xray male face
Cases and figures. Figure 1: cranial landmarks. Figure 2: skull positioning lines. Case 1: normal Waters view skull x-ray. Case 2: normal facial bones. Case 3: with zygomatic arch fracture. Case 4: orbital blowout fracture with teardrop sign. Case 5: maxillary and frontal sinusitis.
Head xray stock photo. Image of head, face, clinic, health 29752294
Compare the injured side with the uninjured side. Fractures of the Facial Skeleton. Within the facial skeleton, there are relative areas of strength, which tend to be spared by fractures lines. These are: Alveolar ridge of the maxilla. Nasofrontal process of the maxilla. Body of the zygoma. Fractures of the Orbits.

RxDentistry Radiographic Anatomy of Facial Bones
A facial X-ray is a series of pictures of the bones in the face. One type of facial X-ray (called a paranasal sinus X-ray series) looks at the air-filled cavities (sinuses) around the nose and eyes. A facial X-ray helps find bone fractures, tumors, foreign objects, infections, and abnormal growths or changes in bone structure or size. An X-ray.

Normal Childs Head Xray Foto de stock Getty Images
Image receptor: 10 × 12 inch (24 × 30 cm) lengthwise. The reverse Waters method is used to show the facial bones when the patient cannot be placed in the prone position. Position of patient: • With the patient in the supine position, center the midsagittal plane of the body to the midline of the grid. Position of part: